Run an Existing Magento 2 App with Homebrew Apache on MacOS in 2018 / 2019
Posted on November 19, 2018
Originally published here, also published on Medium.
So, I started working on a new Magento project with my boss this past weekend, and sitting together at a café, it took us about 5 hours to get the site fully working for development. 😂 😂 😂 While Magento provides a lot of powerful tools for building e-commerce sites, it's a beast to get started up, especially if one of you has only done it on Windows, and one of you has a Mac. 😉 I documented everything we sludged through in those 5 hours, and this post was born!
This is a tutorial that boils down the steps that worked for us (trust me when I say there were many steps we took that didn't work), so hopefully it can take you only 30 minutes to an hour 😊
mcrypt and intl PHP Extensions
If you follow some standard Apache PHP 7.1 on-boarding or getting started guide, you will see that everything goes smoothly, until you try to install Magento dependecies with composer update, and find that Magento needs the mcrypt and intl PHP extensions:
Your requirements could not be resolved to an installable set of packages.
Problem 1
- magento/product-community-edition 2.2.5 requires ext-mcrypt * -> the requested PHP extension mcrypt is missing from your system.
- magento/product-community-edition 2.2.5 requires ext-intl * -> the requested PHP extension intl is missing from your system.
- Installation request for magento/product-community-edition 2.2.5 -> satisfiable by magento/product-community-edition[2.2.5].
The MacOS system version of PHP doesn't ship with these! :scream: :scream: :scream:
Luckily, the Homebrew version does!
Homebrew to the Rescue
I'm going to show you how to get up and running developing your Magento app using Homebrew packages. Note that the config files and start commands for Apache, as well as the path to the desired PHP location, are different than the standard system apache commands!
So, before we do anything with brew, we need to shut down the system instance of Apache (mac normally ships with Apache, so let's do this now):
sudo launchctl unload -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/org.apache.httpd.plist
Now we will install the the Homebrew versions of Apache and PHP. And while we're at it, if you don't have it installed already, we will also need composer, the package manager for Magento, so let's just tack that on the end as well:
brew install php71 httpd composer
Edits to Homebrew's Apache httpd.conf
Edit the Homebrew Apache .conf file with:
sudo nano /usr/local/etc/httpd/httpd.conf
Now we need to make some changes to httpd.conf.
Ensure that the PHP module points to the Homebrew version of PHP (not the system version, which doesn't have mcrypt and intl)! and not commented out:
LoadModule php7_module /usr/local/opt/php@7.1/lib/httpd/modules/libphp7.so
and also add:
<FilesMatch \.php$>
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
</FilesMatch>
And then, on the second DocumentRoot / Directory block (don't mess with the first one!), change the path and point it to your root of your Magento project:
DocumentRoot "/Your/Awesome/Magento/Project"
<Directory "/Your/Awesome/Magento/Project">
...
A Magento app may also need AllowOverride rule set to All inside that <Directory> block:
AllowOverride All
And also, for development, the rewrite_module may also need to be activated (if you see you are getting a lot of 404 not found errors on localhost:8080)
LoadModule rewrite_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_rewrite.so
Great. That should be all thats needed for apache to run a Magento app. Now we need to install Magento dependencies using composer, which we installed in the very first step of this tutorial. Navigate to your Magento project root and issue:
composer update
Then it may say that you need to login. If you don't have a Magento account yet, head to their website and sign up. Go right ahead and create a new public / private key pair for a project (at https://marketplace.magento.com/customer/accessKeys/) - Make sure it is for the correct version of Magento.
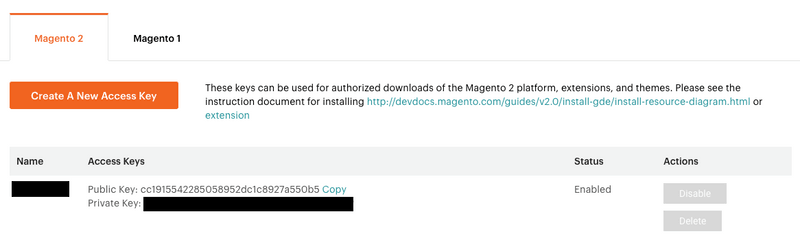
We are going to use these keys right away, because, when the terminal prompts you for first your 'username', this is actually your public key from your Magento account, NOT your Magento email or username. Your 'password' prompt in the terminal is likewise your private key, NOT your Magento login password.
You'll know you've messed up the login to composer if you are getting a big error that looks like this:
[Composer\Downloader\TransportException]
Invalid credentials for 'https://repo.magento.com/packages.json', aborting.
In my opinion this is pretty misleading and should really be changed by the Magento Team.
In the least, Magento will prompt in the terminal if you would like to save those credentials, so you only have to do it once:
Do you want to store credentials for repo.magento.com in /Users/chris/.composer/auth.json ? [Yn]
(I said Y 😊)
Check that everything from composer update looks okay. Everything should be successful, at the worst some warnings at the end.
Checking the Site and Additional Magento Commands
So again, if you haven’t already, start with:
composer update
then enable all the modules:
bin/magento module:enable --all
Then compile the modules:
bin/magento setup:di:compile
If you get a complaint about memory, run bin/magento with the PHP memory option:
php -d memory_limit=512M bin/magento setup:di:compile
To allot 512 Mb to the process (you may find you need more)
Finally, we can navigate to the site. As we left the Homebrew defaults in our apache config, your site should be at localhost:8080. (System Apache is at port 80, but we deactivated it anyway). Magento may then complain that you need to upgrade your modules, something like this:
1 exception(s):
Exception #0 (Magento\Framework\Exception\LocalizedException): Please upgrade your database: Run "bin/magento setup:upgrade" from the Magento root directory.
The following modules are outdated:
[redacted] schema: current version - 1.0.7, required version - 1.0.8
[redacted] data: current version - 1.0.7, required version - 1.0.8
Just do what it says with:
bin/magento setup:upgrade
In your root directory. That’s it! You should be all set to get developing with your Magento site on localhost:8080!
Additional Troubleshooting and Useful Info
If, after all this config, you are getting something similar to this error on localhost:8080:
Authentication plugin 'caching_sha2_password' cannot be loaded: dlopen(/usr/local/mysql/lib/plugin/caching_sha2_password.so, 2): image not found
The SQL user with which Magento interacts with its databases needs to use the legacy version of logging in. If you've created your user with MySQL workbench for example, the default login setting may instead be with a cached sha2 password. We can change this for our SQL user with (within a SQL terminal):
ALTER USER 'putYourMagentoSQLUsernameHereIncludingQuotes'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'putYourMagentoSQLUserPasswordHereIncludingQuotes';
If you are getting some weird errors about the generated content, you may need to clean the cache, delete generated/ and var/ folders, and change permissions on them (this would be in the root of your Magento project):
bin/magento cache:clean && rm -r ./generated/ && mkdir ./generated && chmod -R 777 ./generated && rm -r ./var/ && mkdir ./var && chmod -R 777 ./var
Httpd.conf for Reference
For reference, here is the entirety of my httpd.conf file that is currently working (I have changed only the folder name to respect the name of the project client):
#
# This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
# See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information.
# In particular, see
# <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html>
# for a discussion of each configuration directive.
#
# Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding
# what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure
# consult the online docs. You have been warned.
#
# Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many
# of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the
# server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin
# with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so "logs/access_log"
# with ServerRoot set to "/usr/local/apache2" will be interpreted by the
# server as "/usr/local/apache2/logs/access_log", whereas "/logs/access_log"
# will be interpreted as '/logs/access_log'.
#
# ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's
# configuration, error, and log files are kept.
#
# Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point
# ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the
# Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the
# same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at
# least PidFile.
#
ServerRoot "/usr/local/opt/httpd"
#
# Mutex: Allows you to set the mutex mechanism and mutex file directory
# for individual mutexes, or change the global defaults
#
# Uncomment and change the directory if mutexes are file-based and the default
# mutex file directory is not on a local disk or is not appropriate for some
# other reason.
#
# Mutex default:/usr/local/var/run/httpd
#
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost>
# directive.
#
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
# prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses.
#
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 8080
#
# Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support
#
# To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you
# have to place corresponding `LoadModule' lines at this location so the
# directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used.
# Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l') do not need
# to be loaded here.
#
# Example:
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
#LoadModule mpm_event_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_mpm_event.so
LoadModule mpm_prefork_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_mpm_prefork.so
#LoadModule mpm_worker_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_mpm_worker.so
LoadModule authn_file_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_file.so
#LoadModule authn_dbm_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_dbm.so
#LoadModule authn_anon_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_anon.so
#LoadModule authn_dbd_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_dbd.so
#LoadModule authn_socache_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_socache.so
LoadModule authn_core_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authn_core.so
LoadModule authz_host_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_host.so
LoadModule authz_groupfile_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_groupfile.so
LoadModule authz_user_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_user.so
#LoadModule authz_dbm_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_dbm.so
#LoadModule authz_owner_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_owner.so
#LoadModule authz_dbd_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_dbd.so
LoadModule authz_core_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authz_core.so
#LoadModule authnz_fcgi_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_authnz_fcgi.so
LoadModule access_compat_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_access_compat.so
LoadModule auth_basic_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_auth_basic.so
#LoadModule auth_form_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_auth_form.so
#LoadModule auth_digest_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_auth_digest.so
#LoadModule allowmethods_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_allowmethods.so
#LoadModule file_cache_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_file_cache.so
#LoadModule cache_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_cache.so
#LoadModule cache_disk_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_cache_disk.so
#LoadModule cache_socache_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_cache_socache.so
#LoadModule socache_shmcb_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_socache_shmcb.so
#LoadModule socache_dbm_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_socache_dbm.so
#LoadModule socache_memcache_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_socache_memcache.so
#LoadModule watchdog_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_watchdog.so
#LoadModule macro_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_macro.so
#LoadModule dbd_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dbd.so
#LoadModule dumpio_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dumpio.so
#LoadModule echo_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_echo.so
#LoadModule buffer_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_buffer.so
#LoadModule data_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_data.so
#LoadModule ratelimit_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_ratelimit.so
LoadModule reqtimeout_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_reqtimeout.so
#LoadModule ext_filter_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_ext_filter.so
#LoadModule request_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_request.so
#LoadModule include_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_include.so
LoadModule filter_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_filter.so
#LoadModule reflector_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_reflector.so
#LoadModule substitute_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_substitute.so
#LoadModule sed_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_sed.so
#LoadModule charset_lite_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_charset_lite.so
#LoadModule deflate_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_deflate.so
#LoadModule xml2enc_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_xml2enc.so
#LoadModule proxy_html_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_html.so
#LoadModule brotli_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_brotli.so
LoadModule mime_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_mime.so
LoadModule log_config_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_log_config.so
#LoadModule log_debug_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_log_debug.so
#LoadModule log_forensic_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_log_forensic.so
#LoadModule logio_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_logio.so
LoadModule env_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_env.so
#LoadModule mime_magic_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_mime_magic.so
#LoadModule expires_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_expires.so
LoadModule headers_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_headers.so
#LoadModule usertrack_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_usertrack.so
#LoadModule unique_id_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_unique_id.so
LoadModule setenvif_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_setenvif.so
LoadModule version_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_version.so
#LoadModule remoteip_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_remoteip.so
#LoadModule proxy_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy.so
#LoadModule proxy_connect_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
#LoadModule proxy_ftp_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_ftp.so
#LoadModule proxy_http_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_http.so
#LoadModule proxy_fcgi_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_fcgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_scgi_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_scgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_uwsgi_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_uwsgi.so
#LoadModule proxy_fdpass_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_fdpass.so
#LoadModule proxy_wstunnel_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
#LoadModule proxy_ajp_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_ajp.so
#LoadModule proxy_balancer_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_balancer.so
#LoadModule proxy_express_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_express.so
#LoadModule proxy_hcheck_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_proxy_hcheck.so
#LoadModule session_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_session.so
#LoadModule session_cookie_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_session_cookie.so
#LoadModule session_crypto_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_session_crypto.so
#LoadModule session_dbd_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_session_dbd.so
#LoadModule slotmem_shm_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_slotmem_shm.so
#LoadModule slotmem_plain_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_slotmem_plain.so
#LoadModule ssl_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_ssl.so
#LoadModule dialup_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dialup.so
#LoadModule http2_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_http2.so
#LoadModule md_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_md.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_byrequests_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_lbmethod_byrequests.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bytraffic_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_lbmethod_bytraffic.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_bybusyness_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_lbmethod_bybusyness.so
#LoadModule lbmethod_heartbeat_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_lbmethod_heartbeat.so
LoadModule unixd_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_unixd.so
#LoadModule heartbeat_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_heartbeat.so
#LoadModule heartmonitor_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_heartmonitor.so
#LoadModule dav_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dav.so
LoadModule status_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_status.so
LoadModule autoindex_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_autoindex.so
#LoadModule asis_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_asis.so
#LoadModule info_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_info.so
#LoadModule suexec_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_suexec.so
<IfModule !mpm_prefork_module>
#LoadModule cgid_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_cgid.so
</IfModule>
<IfModule mpm_prefork_module>
#LoadModule cgi_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_cgi.so
</IfModule>
#LoadModule dav_fs_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dav_fs.so
#LoadModule dav_lock_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dav_lock.so
#LoadModule vhost_alias_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_vhost_alias.so
#LoadModule negotiation_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_negotiation.so
LoadModule dir_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_dir.so
#LoadModule actions_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_actions.so
#LoadModule speling_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_speling.so
#LoadModule userdir_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_userdir.so
LoadModule alias_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_alias.so
LoadModule rewrite_module lib/httpd/modules/mod_rewrite.so
LoadModule php7_module /usr/local/opt/php@7.1/lib/httpd/modules/libphp7.so
<FilesMatch \.php$>
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
</FilesMatch>
<IfModule unixd_module>
#
# If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run
# httpd as root initially and it will switch.
#
# User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as.
# It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for
# running httpd, as with most system services.
#
User _www
Group _www
</IfModule>
# 'Main' server configuration
#
# The directives in this section set up the values used by the 'main'
# server, which responds to any requests that aren't handled by a
# <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for
# any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file.
#
# All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers,
# in which case these default settings will be overridden for the
# virtual host being defined.
#
#
# ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be
# e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such
# as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com
#
ServerAdmin you@example.com
#
# ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself.
# This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify
# it explicitly to prevent problems during startup.
#
# If your host doesn't have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here.
#
#ServerName www.example.com:8080
#
# Deny access to the entirety of your server's filesystem. You must
# explicitly permit access to web content directories in other
# <Directory> blocks below.
#
<Directory />
AllowOverride none
Require all denied
</Directory>
#
# Note that from this point forward you must specifically allow
# particular features to be enabled - so if something's not working as
# you might expect, make sure that you have specifically enabled it
# below.
#
#
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
DocumentRoot "/Users/chris/enterprise/awesome-magento-app"
<Directory "/Users/chris/enterprise/awesome-magento-app">
#
# Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All",
# or any combination of:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#
# Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All"
# doesn't give it to you.
#
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords:
# AllowOverride FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
#
AllowOverride All
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
Require all granted
</Directory>
#
# DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory
# is requested.
#
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.php index.html
</IfModule>
#
# The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being
# viewed by Web clients.
#
<Files ".ht*">
Require all denied
</Files>
#
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost>
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost>
# container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here.
#
ErrorLog "/usr/local/var/log/httpd/error_log"
#
# LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log.
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
#
LogLevel warn
<IfModule log_config_module>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
<IfModule logio_module>
# You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" %I %O" combinedio
</IfModule>
#
# The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format).
# If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost>
# container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do*
# define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be
# logged therein and *not* in this file.
#
CustomLog "/usr/local/var/log/httpd/access_log" common
#
# If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information
# (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive.
#
#CustomLog "/usr/local/var/log/httpd/access_log" combined
</IfModule>
<IfModule alias_module>
#
# Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to
# exist in your server's namespace, but do not anymore. The client
# will make a new request for the document at its new location.
# Example:
# Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar
#
# Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to
# access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot.
# Example:
# Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path
#
# If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will
# require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely
# need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to
# the filesystem path.
#
# ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts.
# ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that
# documents in the target directory are treated as applications and
# run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the
# client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias
# directives as to Alias.
#
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/usr/local/var/www/cgi-bin/"
</IfModule>
<IfModule cgid_module>
#
# ScriptSock: On threaded servers, designate the path to the UNIX
# socket used to communicate with the CGI daemon of mod_cgid.
#
#Scriptsock cgisock
</IfModule>
#
# "/usr/local/var/www/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased
# CGI directory exists, if you have that configured.
#
<Directory "/usr/local/var/www/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<IfModule headers_module>
#
# Avoid passing HTTP_PROXY environment to CGI's on this or any proxied
# backend servers which have lingering "httpoxy" defects.
# 'Proxy' request header is undefined by the IETF, not listed by IANA
#
RequestHeader unset Proxy early
</IfModule>
<IfModule mime_module>
#
# TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from
# filename extension to MIME-type.
#
TypesConfig /usr/local/etc/httpd/mime.types
#
# AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration
# file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types.
#
#AddType application/x-gzip .tgz
#
# AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress
# information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this.
#
#AddEncoding x-compress .Z
#AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you
# probably should define those extensions to indicate media types:
#
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers":
# actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server
# or added with the Action directive (see below)
#
# To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories:
# (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.)
#
#AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
# For type maps (negotiated resources):
#AddHandler type-map var
#
# Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client.
#
# To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI):
# (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.)
#
#AddType text/html .shtml
#AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml
</IfModule>
#
# The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the
# contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile
# directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located.
#
#MIMEMagicFile /usr/local/etc/httpd/magic
#
# Customizable error responses come in three flavors:
# 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects
#
# Some examples:
#ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo."
#ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html
#ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl"
#ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html
#
#
# MaxRanges: Maximum number of Ranges in a request before
# returning the entire resource, or one of the special
# values 'default', 'none' or 'unlimited'.
# Default setting is to accept 200 Ranges.
#MaxRanges unlimited
#
# EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it,
# memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver
# files. This usually improves server performance, but must
# be turned off when serving from networked-mounted
# filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise
# broken on your system.
# Defaults: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off
#
#EnableMMAP off
#EnableSendfile on
# Supplemental configuration
#
# The configuration files in the /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/ directory can be
# included to add extra features or to modify the default configuration of
# the server, or you may simply copy their contents here and change as
# necessary.
# Server-pool management (MPM specific)
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-mpm.conf
# Multi-language error messages
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-multilang-errordoc.conf
# Fancy directory listings
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-autoindex.conf
# Language settings
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-languages.conf
# User home directories
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-userdir.conf
# Real-time info on requests and configuration
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-info.conf
# Virtual hosts
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf
# Local access to the Apache HTTP Server Manual
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-manual.conf
# Distributed authoring and versioning (WebDAV)
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-dav.conf
# Various default settings
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-default.conf
# Configure mod_proxy_html to understand HTML4/XHTML1
<IfModule proxy_html_module>
Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/proxy-html.conf
</IfModule>
# Secure (SSL/TLS) connections
#Include /usr/local/etc/httpd/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
#
# Note: The following must must be present to support
# starting without SSL on platforms with no /dev/random equivalent
# but a statically compiled-in mod_ssl.
#
<IfModule ssl_module>
SSLRandomSeed startup builtin
SSLRandomSeed connect builtin
</IfModule>
I hope this was useful to those getting started with an existing Magento 2 project on macOS!
Cheers! 🍺
Chris
